Computed Tomography (CT) Scanning
CT scanning is a diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of an x-ray device that rotates around the patient and digital computing to assemble cross-sectional images (or “slices”) of organs or body sections.
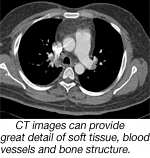
CT differs from conventional x-ray in that it can create highly detailed images of a combination of soft tissue, bone and blood vessels. And it’s generally done with lower doses of radiation than standard x-ray.
64-slice GE LightSpeed VCT
The 64-slice GE LightSpeed VCT computed tomography system in use at Phoebe, produces stunningly detailed images and fast scan times. This innovative system allows us to diagnose a whole host of medical conditions faster and more accurately than ever before.
Such conditions include coronary artery disease, cancer, benign tumors, aneurysms, heart disease, lung disease, vascular disease, kidney problems, liver disease, musculoskeletal disorders, and more.
The 64-slice LightSpeed VCT is used for a multitude of applications, including:
- Neurologic Imaging
- Musculoskeletal Imaging
- CT Coronary Angiography (CTA)
- Cardiac Imaging
- Thoracic and Abdominal Imaging
- Cerebral, Renal, and Peripheral Angiography
- Virtual Colonography
- Lung Scans for Tumors and Pulmonary Nodule
Unlike traditional CT systems, the 64-slice system is capable of showing internal structures of the body with substantially greater anatomic detail. This helps our physicians make an accurate diagnosis and may eliminate the need for other procedures, such as coronary angiography, exploratory surgery, and surgical biopsy.